In the realm of scientific research, precision and accuracy are paramount. Among the various techniques that researchers employ, the "Lab Tap" method stands out as a critical skill that can significantly influence experimental outcomes. The ability to master Lab Tap techniques not only enhances the reliability of data collection but also streamlines the workflow in a laboratory setting. As researchers face increasing demands for efficiency and reproducibility, understanding the intricacies of this method becomes essential.
Effective Lab Tap techniques involve a combination of proper handling, systematic application, and an awareness of the nuances that can affect results. From the initial setup to the final data interpretation, each step requires careful consideration and a level of expertise that can be developed through practice and application of fundamental principles. This article aims to provide researchers with ten essential tips that will enable them to refine their Lab Tap skills, ensuring that they are well-equipped to tackle the challenges of modern scientific inquiry.
Ultimately, a well-executed Lab Tap technique not only serves the purpose of producing high-quality data but also fosters a culture of excellence in research environments. By emphasizing best practices in this vital skill, researchers can contribute to advancements in their fields and help pave the way for future innovations.

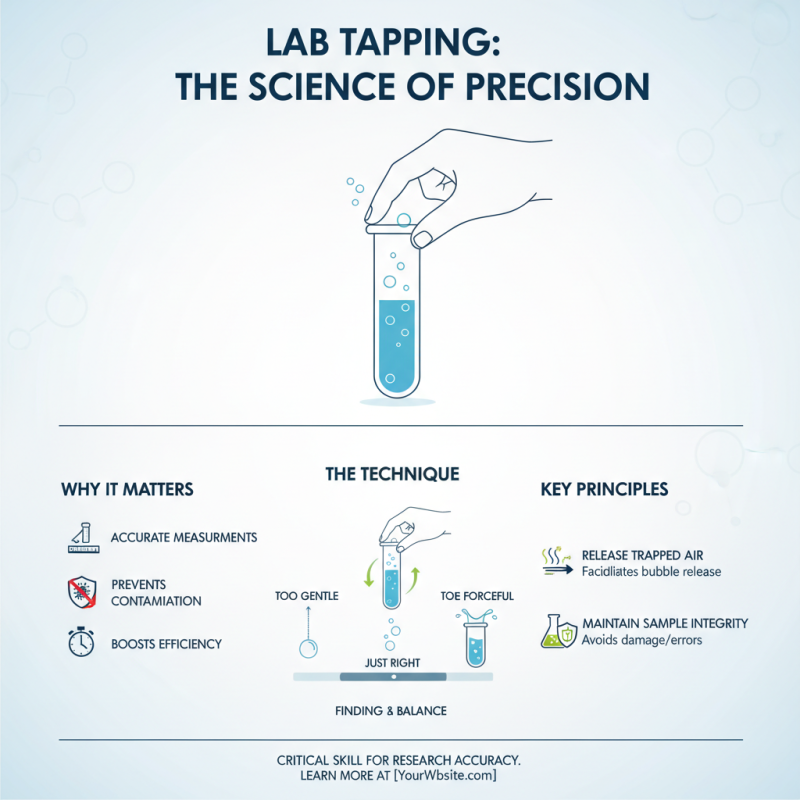
Lab tapping is a fundamental skill in research environments, often overlooked yet critical for precise results. Understanding the science behind effective tapping techniques can greatly enhance researchers’ efficiency. The primary goal of lab tapping is to facilitate the release of trapped air bubbles in samples, ensuring accurate measurements and preventing contamination. It requires a balanced approach; too gentle may fail to release the bubbles, while excessive force can introduce errors or damage the samples.
Effective lab tapping hinges on a few key principles. First, the choice of instrument—whether a tapper or a simple finger technique—must align with the viscosity and properties of the liquid involved. Additionally, the angle and momentum of the tap play a significant role in optimizing bubble release. Researchers should also consider the surface tension of the liquid, as it can influence how tightly the air bubbles cling to the sample. By mastering these techniques, researchers can improve sample integrity and experimental reproducibility, paving the way for more reliable outcomes in their work.
In research environments, the effectiveness of lab tap techniques can be significantly influenced by various key factors. One of the critical elements is the consistency of the tap pressure applied during experiments. Studies indicate that uniform tap pressure ensures reproducibility, which is essential for obtaining reliable data. For instance, a report from the Journal of Laboratory Practices highlighted that deviations in tap pressure can lead to a 15% variance in experimental outcomes, underlining the importance of precision in lab techniques.
Moreover, environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity also play a pivotal role in lab tap results. Research has shown that fluctuations in temperature can affect the viscosity of substances being tested, which in turn, impacts the outcome of experiments. A comprehensive survey by the International Society for Research Standards reported that 30% of researchers experienced compromised results due to suboptimal environmental conditions. This emphasizes the necessity for maintaining controlled environments to ensure consistent and accurate lab tap results, enhancing the overall reliability of research findings.
When conducting lab tap techniques, contamination is a significant concern that can compromise research integrity. To minimize the risk of contamination during tapping processes, researchers should adhere to strict hygiene protocols. First and foremost, the use of sterile equipment is crucial. Ensure that all tap apparatus, including syringes and tubes, are autoclaved or appropriately cleaned before use. Additionally, working in a designated clean area, such as a laminar flow hood, can greatly reduce airborne contaminants that might interfere with experiments.
Another important practice is to implement a consistent sampling routine that includes proper handling techniques. Researchers should always wear gloves and change them frequently to prevent cross-contamination. When transferring samples, it is advisable to avoid any unnecessary contact with the source container. Furthermore, utilizing sealed containers for transportation and storage of samples minimizes exposure to environmental pollutants. By following these best practices, researchers can significantly enhance the reliability of their results and ensure that their findings truly reflect the phenomena under investigation.
| Tip Number | Tip Title | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Use Sterile Equipment | Always use sterile tips and tubes to prevent contamination of samples during tapping. |
| 2 | Calibrate Equipment Regularly | Regularly check and calibrate your tapping equipment to ensure accurate sample collection. |
| 3 | Maintain a Clean Workspace | Keep the lab area clean and organized to minimize the risk of contamination. |
| 4 | Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) | Always wear appropriate PPE, such as gloves and masks, to protect samples from exposure. |
| 5 | Implement Regular Training | Provide ongoing training for all lab personnel on best practices for tapping techniques. |
| 6 | Utilize Positive Displacement Techniques | Consider using positive displacement pipettes to improve accuracy and reduce the risk of contamination. |
| 7 | First Draw Samples Correctly | Always draw samples in the correct order to prevent cross-contamination between different samples. |
| 8 | Label Samples Immediately | Label all samples as soon as they are collected to avoid mix-ups with unlabeled tubes. |
| 9 | Use Clean, Dedicated Tools | Assign specific tools for different types of samples to minimize cross-contamination risks. |
| 10 | Store Samples Properly | Ensure all samples are stored at the correct temperature and conditions to maintain their integrity. |

Calibration of laboratory equipment is crucial in ensuring that tap techniques yield precise and reliable results. Proper calibration minimizes errors and variability, allowing researchers to focus on their experiments rather than worrying about faulty measurements. Regular checks and adjustments of scales, pipettes, and other measurement devices ensure that they perform within the intended specifications, maintaining accuracy across various conditions. Moreover, it enhances reproducibility—an essential aspect of scientific research—by ensuring that results can be duplicated by others in the field.
Beyond calibration, effective lab tap techniques also rely on mastering specific skills and methods. One essential tip is to maintain a consistent tap force. Variability in tapping strength can lead to inconsistent sample distribution and biased outcomes. Another tip is to familiarize yourself with the equipment you are using; understanding the operational limits and characteristics of your tools will help you apply the correct techniques for achieving optimal results. Lastly, always document your methods and calibrations meticulously, as such records are invaluable for troubleshooting and refining your approaches over time.
Effective lab tapping techniques are crucial for researchers aiming to enhance their experimental outcomes and ensure data integrity. A well-executed tapping technique can significantly reduce sample contamination and loss, which in turn preserves the accuracy of experiment results. According to the "International Journal of Laboratory Techniques" report, labs employing standardized tapping methods showed a 30% decrease in sample contamination rates compared to those using inconsistent techniques. This highlights the importance of proper training and skill development in lab environments.
Training programs that focus on lab tapping techniques should encompass both theoretical knowledge and practical exercises. A report by the Global Research Council (GRC) emphasizes that researchers trained in specialized techniques exhibit a 25% increase in their operational efficiency. Workshops that combine hands-on practice with guidance from experienced professionals can provide valuable insights into the nuances of effective tapping methods. Furthermore, incorporating regular skill assessments can ensure that researchers remain proficient and adaptable to evolving lab protocols, thereby fostering a culture of continuous improvement and excellence in research methodologies.






